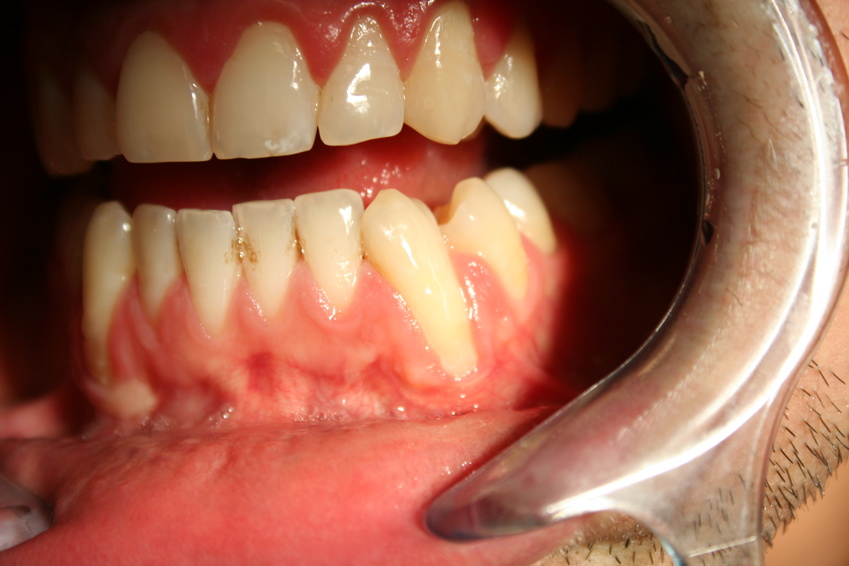
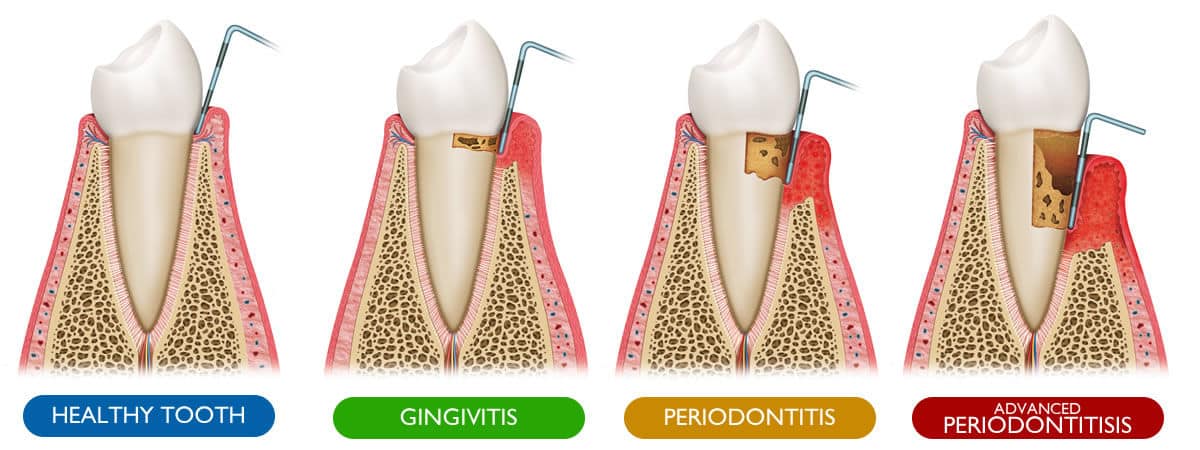
What is Periodontal Disease?
Undoubtedly, dental complications can be frustrating. Apart from causing other health difficulties, dental disorders lower one’s self-esteem. Gum disease is an oral complication that affects the gum’s soft tissues and bones that contribute to teeth support. Typically, the mouth houses a lot of bacteria due to the numerous types of food and other substances that people ingest. Moreover, the mouth has hidden and hard surfaces, which bacteria find the ideal for growth and reproduction. This is the reason health experts recommend that folks should maintain proper oral hygiene. When microorganisms such as bacteria build up on the surfaces and pockets surrounding the teeth, inflammation occurs, and gums are more likely to bleed. During this period, the individual develops a complication known as gingivitis.
Gingivitis is easily treatable, especially when one maintains proper oral hygiene. Untreated gingivitis develops into a periodontal disease that may cause the fall out of teeth due to weak bones and tissues surrounding the teeth. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, periodontal disease and tooth decay are the most prevalent dental complications worldwide. Following reports from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, at least 9% of adults aged between 20 and 70 have gum disease. People with low income are also at risk of having complications due to a lack of finances for professional dental check-up and treatment procedures. The National Institute of Health reveals that the number of men having gum diseases is higher than that of women. The reason behind this is, men rarely go for dental check-ups while women go for more dental check-up visits as they do care about their cosmetic appearance. However, the disease is treatable, even in its most severe state.
The Causes of Periodontal Disease
Smoking
Health statistics show that smoking is the most common cause of periodontitis. Evidence-based studies reveal that current smokers are more likely to experience alveolar bone loss than non-smokers and former smokers who quit smoking more than one or two years ago. Frequent exposure to tobacco impairs the immune system, thus interfering with the periodontal tissue’s ability to heal as required. A compromised immune system makes it harder to fight off gum infections caused by bacteria and other microorganisms. Additionally, smoking lowers the chances of successful treatment for people with periodontitis.
Alcohol
Alcohol harms general health. Pure alcohol has no or little damage to oral health. However, the majority of people do not consume pure alcohol. Liquor, beer, champagne, cocktails, and other mixed alcohol drinks have high levels of sugar. Frequent alcohol consumption is harmful to your gums because the high sugar content feeds the bacteria in your mouth. Therefore, you will be more likely to develop stubborn bacterial infections that progressively damage the gum. Besides, alcohol has strong acidic contents that are corrosive, thus destructive to the gums’ delicate tissue.
Diabetes
Untreated diabetes is an approved risk factor for developing gum disease. This is because diabetes leads to blood vessels’ damage, including the ones that nourish the gums and teeth. Damage of the small blood vessels increases gum infections as there is no enough oxygen and nutrients distributed to the gum. A common symptom associated with diabetes is glycemia (elevated blood sugar level). The high sugar level is a factor that contributes periodontitis as it increases bacteria growth and reproduction. The US National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey shows a high correlation between diabetes and periodontal complication.
Symptoms of periodontal Disesase
The underlying factor of gum disease is the reproduction and growth of bacteria in your mouth. For that reason, you may detect early symptoms of the dental complication if you notice any signs that may associate with bacterial presence. One of the signs you can never miss is inflammation of the gums. This is the most common symptom because, once the body detects a potential infection, the brain sends signals to activate a protective immune response, thus causing inflammation. Bleeding and the presence of pus are also early symptoms of periodontal disease. Here are other symptoms of periodontal disease.
- Loose teeth
- Crooked teeth
- Swollen gums
- Bleeding of gums
- Loss of teeth
- Persistent bad breath
- Painful chewing
- The presence of tartar on teeth
- Change of position of teeth
- Signs of Gum Disease in Children
- Receding gums
- Teeth with abnormal (larger) spacing
- Sore gums
- Presence of pus between the teeth
- Bleeding during brushing
- Altered jaw alignment
Diagnosis of Periodontal Disease
The diagnosis of periodontitis involves a few steps.
Analysis of Patient Health History
The first step of gum disease diagnosis is collecting, recording, and analyzing patient information associated with the complication. For instance, a family history of periodontitis may slightly increase the chances of developing the infection. As mentioned earlier, diabetes is a significant risk factor of having the infection. Patient information about a history of diabetes may help the dentists establish a potential cause of oral complications.
According to medical research, hormonal imbalance is also a potential cause of dental disease. Therefore, a patient will have to give any information regarding medicine use or other issues that lead to hormonal changes, especially for female patients. Nutritional deficiencies are also potential causes of gum infection. Other health complications associated with gum infection include respiratory disease, obesity, cancer, chronic kidney disease, cognitive impairment, and HIV. Patient information concerning any of the complications, as mentioned above, is critical for diagnosis and care.
Physical Examination
Here, a dentist will check for the visible symptoms of periodontal disesase. Crooked teeth, bleeding gums, inflammation, and bad breath will notify the dentist that an individual has oral disease. Longer appearing teeth and a misaligned jawline are important signs during the diagnosis of periodontitis.
The measure of Dental Pockets
Usually, standard dental pockets measure between 1 and 3 millimeters. Pockets that are deeper than 4 millimeters indicate that it is impossible to clean teeth and gums as required, heightening the chances of having gum infection. A dentist uses a probe (small dental ruler) to measure the depth of dental pockets.
Dental X-ray
Some pockets may be too deep, thus impossible to measure using the dental probe. In this case, a dentist an X-ray machine to check for deeper pockets and bone loss. Once a dentist confirms that you have periodontitis, he or she may refer you to a periodontist.
Treating Gum Disease
Treatments for periodontitis vary depending on the extent of the infection. Severe complications require complex treatment procedures, while mild infection can heal through antibiotics or simple home remedies.
Surgical Procedures
Severe infections may require surgical procedures.
Bone Grafts
This procedure involves using synthetic dental implants or the patient’s bones to replace the gums’ lost bones. The procedure supports the teeth while triggering the growth of natural bones to improve tooth stability. Bone grafting is a minor procedure where a dentist makes a small incision on your gums to expose the jaw bone and incorporate a bone material. This, in turn, triggers the creation of new bone cells around the location.
Soft Tissue Grafting
Gum tissues are important in dental health as they support blood vessels that nourish the teeth and gums. Soft tissue grafting is a medical process that restores damaged or lost gum tissue. A dental specialist will use tissue from another part of the mouth to fill the spaces left behind after gum tissue damage. Apart from restoring gum tissue, the procedure also protects teeth against cavities.
Flap Surgery
Flap surgery is a dental treatment procedure that reduces the size of pockets. During the treatment, a dental hygienist lifts back the gums to remove tartar then fits back the gums around the teeth. Flap surgery lessens the chances of bacterial growth.
Medication
Prescription drugs can treat periodontitis by eliminating the bacteria causing infections. There are numerous antibiotic OTC drugs that patients can use to suppress the growth of bacteria. Amoxicillin and metronidazole are common antibiotics used for the treatment of gum infection. A dental specialist may also prescribe antibiotic mouth rinses and gels to treat the complication.
Root Planing
This is a non-surgical treatment process that involves deep cleansing by removing plaque or calculus deep in the roots. Root planing smoothes the root surfaces, therefore eliminating potential hiding places for bacteria and other microorganisms.
Prevention of Gum Disease
Periodontitis is treatable, but there are several ways you can prevent the infection. You need to know how to improve your gum health at home.
Brush Your Teeth at least Twice Daily
Dental hygienists recommend that you should brush your teeth at least twice a day. The goal is to eliminate food particles and other substances that may lead to the growth of bacteria. When you maintain oral hygiene daily, chances of bacterial build up to become minimum. The best option may be using fluoride-based toothpaste, which is effective at maintaining healthy gums.
Floss your Teeth
Brushing your teeth regularly is an effective method of avoiding infections. Nevertheless, there are some hidden locations in the dental formula that are difficult to access. For instance, food particles and other bacterial microorganisms are difficult to eliminate through brushing. That said, you will need more intense cleansing services such as flossing to suppress deep-occurring bacteria. Flossing is an effective dental maintenance practice as it eliminates more than 80% of dental bacteria, including the ones that are deep in the dental roots.
Proper Nutrition
Typically, proper nutrition is a key factor concerning healthy gums. Without proper nutrition, the gums lack healthy vessels to deliver nutrients and oxygen for proper dental functioning. Vitamins, fiber, carbohydrates, and lipids, among other significant nutrients, are critical for proper dental functioning. Hence, one should maintain a healthy diet to provide all the significant nutrients that aid in effective dental health.
Quit Smoking and Excessive Drinking
Smoking and excessive consumption of alcohol weaken the gum tissues that support teeth. Apart from that, alcohol and cigarettes contain corrosive chemicals that lead to crooked teeth and irregular root canals. These factors heighten the probability of developing periodontitis, thus minimizing the chances of having healthy gums. Therefore, you should minimize your smoking and drinking habits to prevent dental gum problems.
Periodontal Disease Treatment in Los Angeles
Periodontitis is a common oral complication. Therefore, there is no reason to have shame regarding the disease. However, this is a serious complication that can lead to other health difficulties later in life. Meet Dr. Delaram Hanookai, a certified dental specialist who has all it takes to correct all your oral complications, including periodontitis. With more than ten years of experience, Dr. Delaram Hanookai boasts of restoring all her patients’ beautiful smiles. Moreover, this dental specialist provides affordable services for gum recession and other treatment procedures concerning periodontitis.
The cost of gum recession treatment procedures varies depending on the type of surgery performed. Gum recession treatments may cause between $400 and $10,000. More so, your dentist may negotiate with insurance companies regarding payment or set up a suitable payment plan depending on your financial circumstances to ensure you have healthy gums.