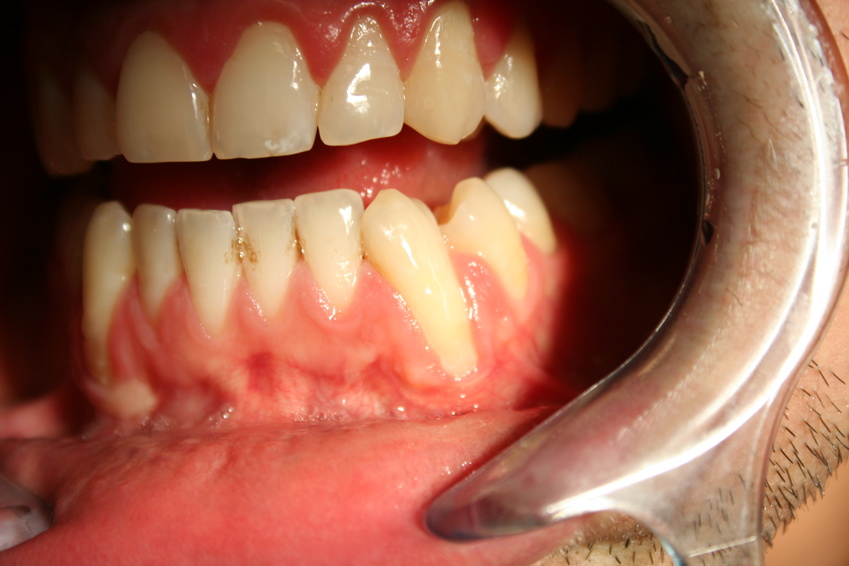
Healthy gums play a crucial role in maintaining optimal oral health and overall well-being. The gums surround and support the teeth, anchoring them in place and protecting the underlying bone and roots. Maintaining healthy gums is essential because they are a cornerstone of good oral hygiene and they contribute to the overall aesthetic appeal.
Understanding Gum Color: What’s Normal?
The color of gums can vary among individuals due to factors like genetics and melanin levels. Melanin is the pigment responsible for skin, hair, and eye color, and it also plays a role in dark gums.
There is a relationship between the color of the gums and ethnicity. In general, people with higher oral melanin levels tend to have dark gums. This means that individuals with African, African-American, or Asian ancestry often have naturally brownish or dark gums.
Therefore, it’s important to ask what does black gums mean to you depending on your ethnicity and genetic diversity. Additionally, gum color can change over time due to various factors, including age, smoking, certain medical conditions, and medications.
Top Causes for Gum Discoloration: A Deep Dive
Pale gums
Pale gums can be indicative of various underlying health conditions. Anemia, a condition characterized by a decreased number of red blood cells or lower hemoglobin levels, is one such health condition associated with pale gums. Hemoglobin is responsible for the red color in blood and contributes to the pink color of healthy gums. In anemic individuals, reduced hemoglobin levels can lead to paleness in the gums.
Teeth bleaching, a cosmetic dental procedure aimed at whitening teeth, can also temporarily affect the appearance of gum color. The bleaching agents used in teeth whitening treatments may irritate the gums, making them paler or lighter in color temporarily.
Red Gums
Red gums can result from various inflammatory processes in the oral cavity and are often accompanied by distinctive symptoms. Here’s an explanation of how inflammation leads to red gums and the associated symptoms:
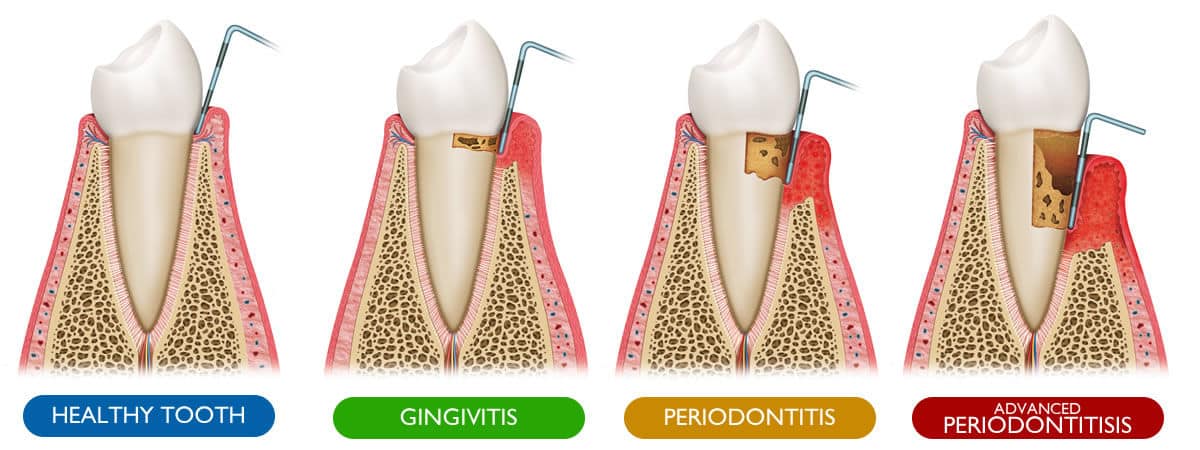
1. Gingivitis:
Gingivitis is a common cause of red gums. It’s an early stage of gum disease characterized by the inflammation of the gingival tissues. The accumulation of plaque, a sticky film of bacteria on the teeth, can irritate the gums, causing them to become red, swollen, and brushing them could trigger bleeding. Los Angeles gingivitis treatment and periodontal infection treatment are some of the services you should seek when you notice any of the above symptoms.
2. Periodontitis:
Periodontitis, a more severe periodontal health issue, can result from untreated gingivitis. In periodontitis, the gum inflammation extends deeper until it reaches the periodontal ligament, cementum and alveolar bone. Red and swollen gums are often accompanied by gum recession, pockets between the teeth and gums, and in some cases, tooth mobility or loss. All periodontal disease stages in LA can be treated through periodontal cosmetic procedures LA like Los Angeles dental deep cleaning and oral bone grafting LA. If you cannot ensure periodontal disease prevention then you should take strict measures to prevent serious periodontal disease implications such as diabetes.
3. Infections:
Bacterial or viral infections can cause localized inflammation in the gums, leading to redness, pain, and swelling. Conditions like oral herpes or bacterial abscesses can result in red and painful gums.
Blue and Bluish-Gray Spots
Bluish-gray spots on the gums or blue gums can be indicative of various underlying conditions, including the effects of certain drugs or poisonings. Here’s an overview of how these factors can contribute to such discoloration:
1. Medications:
Some medications can cause changes in gum color as a side effect. For instance, minocycline, a tetracycline antibiotic, is known to cause a condition called “minocycline-induced hyperpigmentation.” This condition can result in gum hyperpigmentation which is the cause gums turning black or blue-gray.
2. Metals and Poisonings:
Exposure to heavy metals or toxic substances can lead to gum discoloration. For example, chronic exposure to lead, often seen in cases of lead poisoning, can cause bluish-gray discoloration of the gums, known as “lead line.”
White Patches
White patches on gums can be indicative of various oral conditions, including stomatitis, leukoplakia, and thrush, each with its own significance:
1. Stomatitis:
Stomatitis refers to the general inflammation of the oral mucosa, including the gums. It can be caused by viral, fungal or oral bacterial infections, as well as irritants like tobacco or certain medications. Inflammatory changes can result in white patches or sores on the gums. The significance lies in identifying the underlying cause of stomatitis, as it can range from benign conditions like canker sores to more serious infections, such as herpes simplex virus or autoimmune diseases. Treatment and management of the white spots on gums depend on the specific cause.
2. Leukoplakia:
Leukoplakia is a condition characterized by thick, white patches that can develop on the gums and other areas in the mouth. These patches often result from chronic irritation or tobacco use. While leukoplakia itself is benign, it can sometimes progress to show oral cancer signs. Thus, it is of significant concern and should be evaluated by a healthcare professional. Biopsies and lifestyle changes (like quitting smoking) may be recommended.
3. Thrush (Oral Candidiasis):
Thrush is a fungal infection caused by Candida yeast. It can lead to white, cottage-cheese-like patches on the gums and other oral surfaces. Thrush on gums is more common in individuals with weakened immune systems, diabetes, or those taking certain medications such as corticosteroids. While thrush is usually not a severe condition, it may signal early gum disease symptoms and requires treatment with antifungal medications.
Brown and Black Spots
Gums turning black or brown can be attributed to various factors, with smoking and underlying diseases being common causes. Here’s an explanation of how these factors contribute to such discoloration:
1. Smoking:
Tobacco smoke contains numerous harmful chemicals, including tar and nicotine. Smoking can lead to several oral health issues, including:
-Nicotine Staining:
Nicotine effects on gums include formation of yellow or brown spots gums and teeth over time.
-Tar Deposits:
Tar in tobacco smoke can accumulate on the teeth and gums, resulting in brown or black spots on gums.
– Reduced Blood Flow:
Smoking restricts blood circulation, reducing oxygen and nutrient supply to the gum tissues, which can result in dark or black gums.
2. Gum Disease (Periodontitis):
Advanced gum disease, particularly if left untreated, can lead to black gums. This is often due to chronic inflammation, bleeding, and tissue damage associated with periodontitis.
It’s important to note that while smoking is a common cause of gums turning black, unusually black gums should not be ignored, as they may also signal underlying diseases or conditions. There are periodontal clinics Los Angeles, like ourselves, with LA gum disease specialists that can perform regular dental check-ups to identify and address any underlying causes of the issue. If necessary, your dentist may recommend lifestyle changes, treatment for gum disease, or further medical evaluation to rule out serious health issues.
Less Common but Critical Causes for Dark Gums
1. Melanin
Melanin is a natural pigment produced in the body that gives color to the skin, hair, and eyes. In the oral cavity, melanin can also be present in varying amounts and concentrations, contributing to the color of the gums. Some individuals naturally have higher levels of melanin in their gum tissues, resulting in darker brown or black gums.
However, changes in the color or the formation of black spot on gums should be taken seriously and evaluated by a periodontist or a dental professional. While gum melanin is a common reason for dark gums or black gums around teeth, gums turning black suddenly, the appearance of new black spot on gums, or changes in the gums’ color can sometimes indicate an underlying issue.
If you are in a state like LA, a Los Angeles periodontist can conduct a thorough examination, diagnose the cause of gum color changes, and recommend appropriate treatment to ensure optimal oral health and overall well-being.
2. Smoker’s Melanosis
Smoking has a noticeable and detrimental impact on gum color due to the harmful substances found in tobacco products. The chemicals present in tobacco, such as nicotine and tar, play a significant role in altering the appearance of gums. Here’s how smoking affects gum color:
1. Nicotine Staining:
Nicotine, a key component of tobacco, is absorbed into the bloodstream during smoking. Over time, this nicotine can stain the gums and teeth, leading to yellow or brown gums.
2. Reduced Blood Flow:
Smoking reduces blood narrows resulting in less blood circulation to the gums. The decreased blood supply results in oxygen and nutrient deprivation to the gum tissues, resulting in discolored or black gums. This leads to a layer of black gums around teeth.
3. Tar Accumulation:
Tar, a residue from burning tobacco, is a sticky substance that can accumulate on the teeth and gums. It adheres to the surfaces, causing black or brown gums.
4. Inflammation and Gum Disease:
Smoking is a significant risk factor for gum disease (periodontitis). It causes inflammation, bleeding, and damage the gum tissue health. This inflammation can lead to changes in gum color, making them look redder and more pronounced which is a clear sign of lack of dental consultation oral care routine.
5. Delayed Healing:
Smoking slows down the healing process in the oral cavity, making it harder for the gums to recover from damage caused by infection, injury, or dental procedures. This delay in healing can affect the overall appearance and health of the gums.
Smoking not only stains the gums due to nicotine and tar but also leads to reduced blood flow, inflammation, and delayed healing, all of which contribute to changes in gum color and overall deterioration of oral health. In this case, one of the gum treatments in Los Angeles would be to quit smoking as one of the oral care best practices.
3. Addison’s Disease
Addison’s disease, also known as primary adrenal insufficiency, is a rare disorder characterized by insufficient production of hormones by the adrenal glands, primarily cortisol and aldosterone. These hormones play a vital role in regulating various bodily functions, including metabolism, blood pressure, and the body’s response to stress.
These adrenal gland disorders cause reduced production of cortisol and aldosterone due to autoimmune damage, infections, or other underlying causes. This hormonal imbalance can manifest in several ways with gum disease symptoms Los Angeles being on the list.
One of the noticeable signs of Addison’s disease is hyperpigmentation or darkening of the skin and mucous membranes. This occurs due to elevated levels of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), which stimulates the production of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin, hair, and eye color. Hormonal gum changes lead to the overstimulation of melanocytes, resulting in the darkening of the gums.
As a result, individuals with Addison’s disease may have their gums turning black. Others may start to develop brown spots on gums. This discoloration is a direct consequence of the hormonal imbalance affecting melanin production. It’s essential for individuals with suspected symptoms of Addison’s disease, including changes in gum color, to seek medical evaluation and appropriate treatment to manage the condition and its effects on hormonal regulation and pigmentation.
4. Acute Necrotizing Ulcerative Gingivitis (Trench Mouth)
Acute Necrotizing Ulcerative Gingivitis (ANUG), commonly known as “Trench Mouth,” is a severe and painful gum infection characterized by a sudden onset of symptoms. It causes gum ulcers and can lead to significant discomfort if left untreated.
Symptoms:
1. Severe Gum Pain:
ANUG causes intense gum pain that can be throbbing and constant, making chewing and even speaking challenging.
2. Bleeding Gums:
Gums often bleed spontaneously or when brushing and flossing.
3. Foul Breath:
The infection can result in bad breath (halitosis).
4. Swollen Gums:
The gums may become swollen and appear red or purplish in color.
5. Pseudomembranes:
A film with gray or white spots on gums can appear.
Causes:
ANUG is usually caused by an overgrowth of certain oral bacteria, often in response to a weakened immune system or poor oral hygiene. Stress, smoking, malnutrition, and underlying health conditions can contribute to its development.
Treatment:
Treatment of ANUG typically involves:
1. Antibiotics:
A healthcare provider may prescribe antibiotics, such as metronidazole or amoxicillin, to combat the bacterial infection.
2. Pain Relief:
Over-the-counter pain relievers or prescription medications may be recommended to manage pain and inflammation.
3. Oral Hygiene:
Improved oral hygiene practices, including gentle brushing and rinsing with an antimicrobial mouthwash, are crucial.
4. Dietary Changes:
A diet rich in vitamins and nutrients can aid in recovery.
5. Stress Management:
Reducing stress levels can help prevent recurrences.
Prompt diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent the infection from progressing to more severe oral and systemic health problems.
5. Amalgam Tattoos
Amalgam tattoos in dental procedures refer to dark, bluish-gray or black spot on gums or patches that appear on the oral tissues, such as the inside of the cheek. These tattoos are typically caused by the accidental embedding of tiny metal particles, often from dental amalgam fillings, into the gums during dental procedures. While they may appear concerning, amalgam tattoos are generally harmless and rarely cause any symptoms. The significance lies in their potential to mimic other oral conditions like melanoma or other pigmented lesions, leading to misdiagnosis. Through periodontal screening, dental professionals can differentiate an amalgam tattoo from more serious gum disease risks periodontal disease signs like those of melanoma. It’s essential for patients to inform their dentists about previous dental work to ensure accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment planning for gum rejuvenation.
6. Medication-Induced Discoloration
Medications like Minocycline, commonly used to treat acne and bacterial infections, can lead to oral health and wellness concerns such as the gum turning black or bluish gray. The extent of discoloration can vary among individuals. While it’s generally harmless, it can be distressing. Discontinuing the medication or switching to an alternative treatment, under a healthcare provider’s guidance, may help alleviate or prevent further medication-induced gum discoloration.
At-Home Remedies: Lightening Dark Gums Safely
If you aim to maintain gum health, it’s advisable to seek guidance from a healthcare professional.
1. Overview of potential herbal remedies and their effectiveness.
While attempting to make black gums pinker, some people may consider utilizing medicinal herbs like sage, mint, lemon balm, and oregano. Alternative medicine suggests thyme, calamus root, chamomile, and sage for gum care. Preparing a decoction from these herbs may help alleviate gum pain, reduce inflammation, strengthen tissues, and combat bad breath.
2. Warnings and recommendations before trying home remedies.
These gum disease remedies can prevent mouth inflammation; however, their effectiveness as gum discoloration solutions in treating black gums remains uncertain as there may be persistent black spot on gums.
3. Visit a specialist
If you’re interested in trying these remedies as gum discoloration treatments, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare expert like Dr. Hanookai who is a periodontist and specialist in gum treatment for evaluation before proceeding.
Professional Interventions: Achieving Pinker Gums
Gum Bleaching/Depigmentation
Gum depigmentation, or bleaching, part of professional gum treatments, is a cosmetic procedure used in gum lightening. It involves the removal of excess pigmentation from the gums using lasers or surgical techniques. Results are visible immediately or within a few weeks, with improved gum aesthetics.
The two most common gum discoloration methods used are microdermabrasion and Laser Techniques. Microdermabrasion for gums uses abrasive particles to exfoliate pigmented gum tissue and is suitable for milder cases such as a small black spot on gums. Laser gum treatment techniques, more precise and effective, utilize dental lasers to remove pigmentation, making them a preferred choice of gum bleaching Los Angeles for deeper or stubborn discoloration. Selection between the stated gum depigmentation methods depends on the severity of gum pigmentation.
At Southland Dental Care we take a comprehensive approach to gum treatments, ensuring optimal outcomes and patient satisfaction.
From Gum Discoloration to Tooth Loss: The Silent Progression
Although gums turning black is primarily a cosmetic issue, it can also signal underlying dental problems. Neglected, these issues can cause substantial damage in the oral cavity. However, some of these issues can be solved through gum surgery Los Angeles and periodontal maintenance LA services offered in Los Angeles gum health care centers.
Gum Discoloration: A Symptom Not to Ignore
While dark gums might seem cosmetic or natural, sudden changes in gum color can indicate significant health issues. Conditions like Acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis or amalgam tattoos signify underlying problems that require prompt attention.
Ignoring these symptoms endangers both the aesthetics of your smile and the stability of tooth-supporting structures. As these support systems weaken, the chances of losing a tooth escalate.
Saving Your Smile with Southland Dental Care
In the unfortunate event of tooth loss, it’s crucial to know that modern dentistry, particularly at Southland Dental Care, can fully restore both the look and function of your teeth. Dental implants Los Angeles provide durable, long-term replacements, preserving your smile and overall oral health.
In LA we offer a range of oral care services such as teeth scaling and root planing LA, Los Angeles periodontal therapies, gum grafting Los Angeles, periodontitis treatment LA and gum disease prevention Los Angeles. Other cosmetic periodontal procedures we offer are periodontal examinations in LA to determine dark gums causes. Once the cause is determined, we offer the appropriate solution which may include periodontal laser therapy Los Angeles to prevent the periodontal disease progression.
On the path from noticing gums turning black or formation of a black spot on gums, to achieving excellent dental health, you can rely on Southland Dental Care as your trusted companion. With individualized periodontal care we are able to focus on early detection, treatment of black spot on gums and other oral pigmentation disorders, and on the restoration and preservation of your radiant smile.
You should visit Southland Dental Care, Dr. Delaram Hanookai. We treat black gums besides providing free consultations and second opinions, backed by 28 years of experience in oral health maintenance. Plus, qualified patients can enjoy free transportation. Contact us to check your eligibility.
Conclusion: Prioritizing Gum Health
Regular dental check-ups are essential for detecting and addressing oral health care problems early, preventing gum discoloration concerns later on. Oral health education about proper dental care practices, dental health innovations, and potential risks helps you make informed choices for your oral health and helps you learn answers to critical questions such as what causes black gums. You also learn how to get rid of black gums. These help you carry out comprehensive gum care using the right dental health practices, maintain your oral tissue health care routine and prevent periodontal infection.
As a way of keeping yourself informed you can also learn about advanced gum disease gum health awareness, oral inflammation oral melanin production gum depigmentation procedures and advanced periodontal therapies modern gum treatments.
By prioritizing check-ups and staying up-to-date, you can maintain a beautiful, healthy smile and prevent complications that may affect your overall well-being.