An abutment is one of several other dental procedures that help to protect your teeth from further damage. This article describes a dental abutment in-depth, how it is fitted, and the ideal aftercare.
What Is an Implant Abutment?
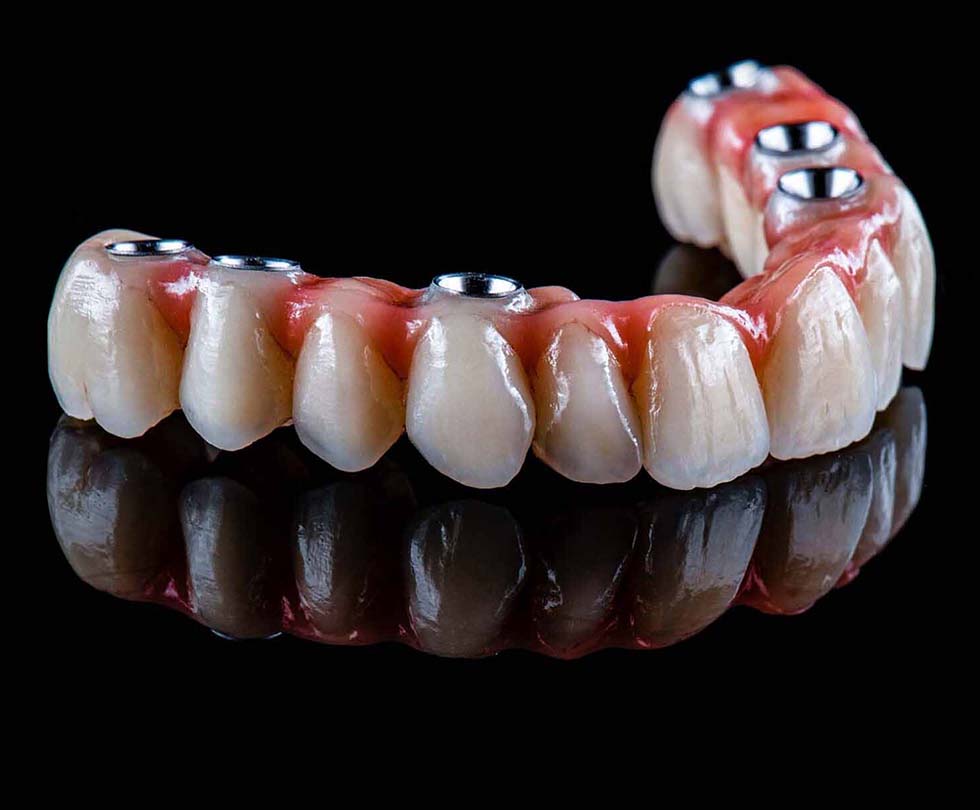
Abutements are metal connections that your dentist will insert into your dental implant once you have healed from dental surgery. A dental implant abutment is a tiny piece of zirconia, titanium, and sometimes gold that connects the dental implant to the crown or other dental treatment. Because the abutment’s materials impact its strength and appearance, choosing the correct one for the task is important. Zirconia is more popular as its similarity to the natural tooth color makes it more preferable as it is less visible.
It serves as a link, but it also aids in shaping the gums surrounding the dental repair in a healthy and aesthetically attractive manner.
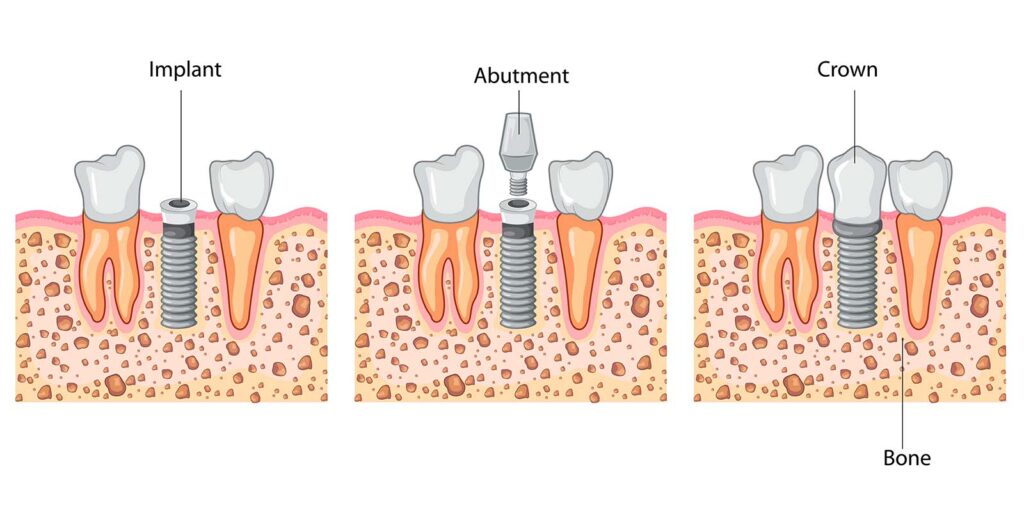
What Is an Abutment in Dentistry?
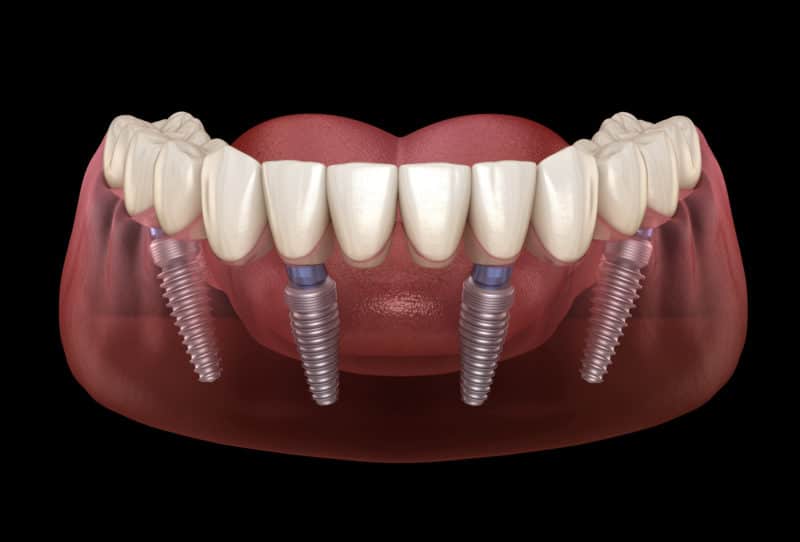
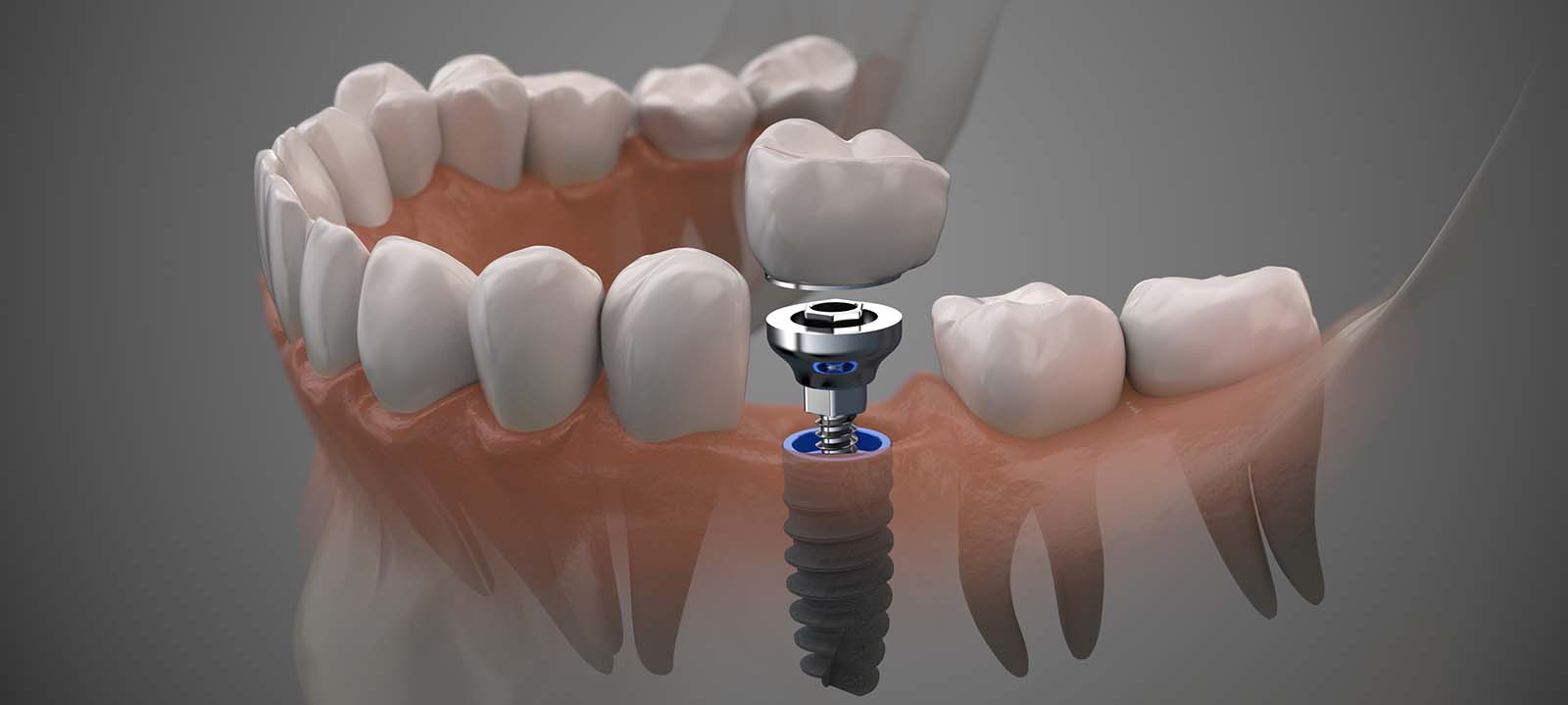
A tooth implant abutment is a piece of dental hardware that connects two teeth. This term is employed in the scope of dental implants, a fixed bridge, or partly removable dentures. A dental implant is a metal structure that looks like a tooth root. When your dental surgeon inserts your dental implant, a metal component acts as a foundation for the crown. It is referred to as an abutment.
These metal implants act as a link, with one end connecting to your jawbone just below your gum and the crown placed on the other. The osseointegrated implant fixture looks like a screw. Osseointegration is the process by which the metal gets attached to your bone. As a result, dental implants give the same level of support for your abutment and crown as natural teeth.
What Is the Purpose of Abutements?
Regeneration of damaged gum tissue is sometimes enabled using abutements. Healing cuffs are another name for them. Healing abutements go on the dental implant or crown, and because they are larger than crown, they create room for the crown on the gum.
Implant and abutment crown placement is a delicate process that needs to be done with the utmost precision to avoid further damage to the remaining teeth. An abutment crown provides aesthetic appeal for those who have damaged teeth.
Different Types of Abutements For Dental Implants
The different types of abutements are made from different materials. There are prefabricated abutements and custom-made ones.
Prefabricated abutments
Prefabricated abutements are stock manufactured in a variety of shapes and sizes. Therefore, the manufacturing company will often pair them with the implants. Your dentist will then choose those that are best suited for dental care. A prefabricated abutment and crown can be made from titanium, gold, surgical stainless steel, or zirconium.
- Titanium abutments– these are made from titanium alloys and are very strong and compatible with the biological makeup of the gum tissue. As a result, they rarely cause an adverse allergic or rejection reaction. Dentists also prefer using them for molars and premolars because they last long. The titanium alloys can withstand the long-term sustained pressure from chewing and will not wear out fast.
- Gold alloy abutments– an implant abutment crown made from gold alloy is used especially for people who suffer from titanium alloy reactions. In itself, gold is a strong and durable metal, which makes it an excellent option. The one disadvantage with these kinds of abutements is that they are visible.
- Zirconium abutements– made from zirconium, a ceramic-like material, are fast becoming the most popular choice. The reason for this is because they are the same color as the teeth, which camouflages them. Zirconium is highly durable and biocompatible, which are other reasons why it is so popular.
Custom Made Abutments
Custom-made abutements are made from taking impressions of the implant. The impression is made from the teeth next to the implant tooth and gingiva. The design restoration is then made at the dental laboratory to the size and exact shape of the impression. Custom-made abutements will be made from zirconium, titanium alloys, or other metal alloys.
How Abutments Are Chosen
Before you have the procedure, you can ask your dentist what abutment they will use and why. The dental professional will explain to you the choice of dental abutment and why. This choice is based on some factors, which include:
- The kind of dental implant that the dentist will use, whether a fixed bridge, crown, or a denture
- The position of the implant in the mouth where metal alloy abutements are preferred for molar and premolar implants. The reason for this is because of the chewing force that is used. Dentists will use a smaller implant abutment and crown for the front part of the teeth because the surface area is small.
- The method by which the abutements and the implant are joined together. It can be done using dental cement, lag screws, or special retainers.
When choosing the kind of dental connectors to use, these are considered to ensure that the implant will last long and with little side effects and discomfort in the area of operation.
How Abutments Are Fitted
There are two options to attach an implant into the jawbone successfully. After the abutment is fitted into the mouth, the gum tissue closes over it and heals. In the meantime, it is fusing with the jawbone to give a firm surface for the implant to latch on. When the jawbone and the gum have completely healed, the dentist will then cut the gum open to expose the abutment so that the dental implant can be fixed onto it. The gum tissue then naturally closes around the abutment but does not cover it. The implant will be fixed on this jutting part.
Another option is using a healing abutment. Because it is larger than the implant, the gum tissue heals around it, creating space for the implant. Using a healing cuff is preferred because the dentist will not need to cut the gum again as it heals around the implant.
When the implant has completely merged with the jawbone, the dentist will remove the healing cuff. The crown is then fitted on the abutment. Afterward, the gum tissue is reshaped to match the crown perfectly. It is done to ensure the crown fits into the space created by the healing cuff. The abutment crown, in this case, is visible as it passes the gum. It will take another two weeks for the gum tissue to heal before the crown is fixed.
Benefits of Using A Healing Abutment
The difference between an abutment and an implant is the position on the gum line. Implants go below the gum line, so they are invisible. On the other hand, abutements are above the gum line, making them visible.
Using a healing cuff does not necessitate you having a visible abutment. It also does away with the extra dental surgery. This is because the dental surgeon will not have to cut open the gum again to expose the abutment.
Reshaping the gum, which happens with a healing cuff, is not a surgical procedure. Rather, it is an outpatient procedure that does not take long and heals after a short period.
Caring For Abutments
After your procedure, gums will take between four to six weeks to heal around the placed tooth implant abutment. Your dentist will give you care instructions based on cleaning the area and your oral hygiene. Other additional advice will be around what kinds of foods to eat and what to look out for as signs of infection.
Cleaning
We recommend rinsing the area with an antibiotic rinse or warm, salty water in the first two weeks. These treatments will help kill any bacteria from food that gets lodged in the area. You can brush your teeth but do not brush the area near the healing site or surrounding areas. It is to prevent accidentally opening up the wound further.
As the wound continues to heal in the next two weeks, you can wipe the implant abutment crown site. We especially recommend this if there are food and plaque deposits in the area. Use a piece of gauze dipped into the antibacterial mouthwash or in warm, salty water and gently wipe the area. Do not apply pressure even if food particles seem stuck. It is better to alternate between wiping the area and rinsing until all the food particles are removed.
After one month, the healing abutment crown area should have sufficiently healed so that you can brush it gently. Use a soft-bristled brush and brush gently to remove any food and plaque.
Foods To Eat And Chewing
It is recommended that you do not eat hard, chewy foods. These foods will cause bruising, leading to infection around the abutment and crown. Avoid chewing with the side of your mouth where the abutment crown has been placed.
Chewing or biting with this side will interfere with the fusing process of the abutment and the jawbone. The jarring movements will make the fusion take a longer time. It is also uncomfortable to use that area as it may be tender from placing the healing cuff into the gum.
What To Look Out For
After an abutment crown placement, you will need to call your dentist to get quick treatment if you see any of these signs. These include
- A healing cuff that is loose or comes off
- Continuous bleeding even with gentle treatment of the site
- Pain in the jaws, gum, mouth that the prescription medication does not cure
- High fever and a very sore site area
What To Expect After The Procedure
After every stage of the implant abutment and crown surgeries, there will be some discomfort. The normal discomfort to expect include:
- Soreness and pain in the site of the implant that is managed by the prescription medication given
- Swelling of the gum around the area and the face
- Bruising of the gums, skin, and internal and sometimes external cheek area around the surgery site
- Some bleeding will stop within the day
How The Crown Is Connected To the Abutment
The dentist will attach the crown onto the implant using the abutment when the gum tissue around the healing cuff has healed successfully. The dentist will make a model of your mouth, teeth, and jaw because it ensures that the dental implant will be comfortable and fit right like your natural teeth.
Custom-fit teeth will be made from impressions of your jaw, teeth, and abutments. The implants are then made from these impressions. Therefore, the implants made will fit perfectly as the bite registration is exactly made for your mouth.
The dentist will then use dental cement to fix the crown in place onto the abutment. During this period, you should not eat hard or crunchy foods to dislodge the crown. If the crown feels uncomfortable or the bit is not aligned, the dentist will make further adjustments until it feels right.
Oral Care For Implants
Once you have successfully finished the process of having an implant and abutment placed, you need to take care of them. Because they are just like natural teeth, they need oral care. Good oral care will ensure they last longer and are healthy, just like natural teeth.
Go for regular dental checkups to ensure that your implants are healthy and remain in good condition. The dentist may recommend taking X-rays to check the bone level around the implant. They may also check the gum tissue around the implant to ensure the whole area is healthy and free of inflammation.
For any questions on what is an abutment in dentistry? And any other dental issues, contact us today and we shall promptly respond to you.
See also: Permanent teeth replacement options